Meaning and Characteristics :
Perfect Competition:
Perfect competition is a market structure in which the following characteristics are found:
1. A large number of buyer and sellers
2. Homogenous Product
3. Free entry and exit of firms in an industry
4. Perfect knowledge of market conditions
5. Firm is a price – taker
6. Perfect mobility of factors of production
7. No transport cost
8. Price, Average Revenue and Marginal revenue are equal ( P = AR = MR ) and they are horizontal to the x – axis.
Equilibrium of the Industry or Price determination :
- Under perfect competition, no single firm or single consumer can influence the market price because of its negligible share in total supply or total demand of the industry.
- Therefore, short run equilibrium price and quantity is determined by the interaction of market demand curve and market supply curve.
- In the given figure, the demand curve DD represents the aggregate demand of all the consumers and supply curve SS represents the total supply of the industry.
- The point of intersection of DD curve and SS curve is the point E represent the short run equilibrium point, where the total market demand is equal to the market supply.
- The equilibrium price is OP and equilibrium quantity is OQ.
- If the price is above OP, say OP1, there is excess supply, which pulls down the price.
- On the other hand, if price is below OP say OP2, there is excess demand, which results in rise in price.
- At equilibrium point E ,there is neither excess supply nor excess demand and therefore, the price has neither a tendency to fall nor a tendency to rise.
Equilibrium of the Firm in the Short Run:
- Under perfect competition, a firm can not influence the market price thus it is price – Taker.
- Under perfect competition, the individual firm is assumed to be facing a perfectly elastic demand for its product, because any variation in output will have such a negligible effect on total supply and market price that it can be said to be zero.
- The price given to all the firms is determined in the industry by the forces of market demand and supply.
- Since the firm is price taker and the demand is perfectly elastic, it means that any variation in production will have no effect on the market price.
- The firm has not to reduce the price to sell more and also it can not sell anything if it charges more than the market price. Means a price – taker firm always sells at market price.
- The firm’s marginal revenue will be equal to average revenue at the level of market price at every level of output and the two would coincide in the same straight line. Thus, Price(P) = AR = MR.
- The short run equilibrium of the firm can be illustrated by combining the short run cost curve with perfectly elastic demand curve (AR curve ) faced by the firm.
- Under perfect competition a firm is a price – taker, it has to decide the amount of output it should produce at the given price, to maximise its profit.
- To determine the profit maximising output, the firm has to fulfill the two equilibrium conditions :
1. First condition for the equilibrium of the firm, in the short – run is, that short run marginal cost must be equal to marginal revenue so
SMC = MR
and SMC curve cuts the MR curve from below.
Since for perfectly competitive firm
MR = AR = Price
Therefore, SMC = MR = Price
This is the profit maximising rule.
2. A perfectly competitive firm, while maximising its profit, may be earning super – normal profit, incurring losses or earns normal profits, depending on its cost and revenue conditions.
A firm in short run will be in equilibrium when –
a. Price or AR < SAC but (AR > AVC) it means that the firm is incurring losses.
b. If AR = SAC , it means that the firm is earning only normal profits.
c. Price or AR > SAC, it means the firm earns abnormal profits.
1. When the firm incurring losses:
In the given figure –
- The ‘U’ – shaped SMC curve intersects the AR = MR =P line at point E from below. The point E is therefore equilibrium point where SMC = MR.
- A perpendicular drawn from point E to the X – axis which determines the equilibrium output OQ and the price at point E is equilibrium price.
- At point E, SAC curve lies above the AR line, therefore the firm is incurring losses, shown in shaded area (BSER) in the figure.
- AR or Price exceeds AVC at point E, therefore the firm is in short -run equilibrium and the firm continues to produce despite losses.
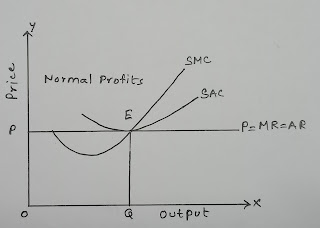
2. When the firm is earning normal Profit:
- The ‘U’ – shaped SMC curve intersects the AR = MR = P line at point E from the below. The point E is equilibrium point and OP and OQ are the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity respectively.
- At point E, P= AR = MR line is tangent to SAC curve it means AR = SAC at this point. The firm covers only its SAC. Therefore, the firm earns normal profit.
3. When the firm earns Super – Normal Profit:
- The ‘U’ – shaped SMC curve intersects the AR = MR = P line at point E from the below. The point E is equilibrium point and OP and OQ are the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity respectively.
- At point E, SAC curve lies below the AR line therefore AR > SAC at point E. This means the firm earns super normal profits shown by the shaded area BSEP.
Supply Curve of the Firm:
- The supply curve of a firm shows various quantities of a commodity a firm is willing to supply at different prices.
- The quantity at which a firm is willing to supply at a particular price is determined by the equality of SMC and MR (= AR =P) .
- In the above figure at price P0 (price P0 = AR0 =MR0), SMC curve cuts MR0 point, which is equilibrium point and OQ0 is equilibrium point and OQ0 is equilibrium quantity.
- At point E0, line AR0 is tangent to AVC curve. Therefore, P0 = AVC it means the firm is able to cover only variable cost.
- Below P0 price, nothing would be produced since P< AVC.
- Point E0 is known as shut – down – point because the firm would not like to operate below this point.
- Shut – down – point is the situation where the firm covers only variable cost i.e., AR (price) = AVC and the firm would not like to operate below this point.
- OQ0 is the minimum supply of the firm in the short run.
- If the price rises to P1, equilibrium shifts to E1 where SMC = MR.
- Since AR1 is tangent to SAC at E1 point, AR = SAC equilibrium quantity also increases to Q1.
- Point E1, where the SMC curve cuts the minimum point of SAC it is known as ‘break – even – point’ because the firm is able to cover all the costs – both variable costs and fixed costs at OP1 price and AR =AC .
- Since at this price AR =AC it is the situation of no – profit – no – loss.
- At this price P1, the firm will supply OQ1 quantity.
- When price is further rises to P2 and P3, equilibrium is set at E2 and E3 respectively and quantity supplied is OQ2 and OQ3 respectively.
- Since in both these prices AR > SAC the firm is earning super – normal – profits.
- That part of the short – run MC curve which lies above the minimum point of AVC curve is the supply curve of the firm in the short – run.
- Since within this range MC curve is sloping upward to the right, the supply curve of the firm in the short run is always upward sloping.
Also Read :





This comment has been removed by the author.